 |
| Credits: NASA |
The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) a.k.a. Kibo is the first contribution of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to the International Space Station (ISS) program.
Kibo improves the research capabilities of the ISS by accommodating a maximum of four astronauts who can conduct scientific research activities and experiments in orbit.
JEM has six major components: the Pressurized Module (PM), the Exposed Facility (EF), the Experiment Logistics Module – Pressurized Section (ELM-PS), the Experiment Logistics Module – Exposed Section (ELM-ES), the Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS), and the Inter-Orbit Communication System (ICS).
The PM is the largest component of JEM. It has a cylindrical shape, 4.4 m in diameter and 11.2 m in length. A total of twenty-three racks can be installed in the PM, six racks on each of the four walls, except for the zenith wall, which can accommodate a maximum of 5 racks. Some of the visible features are the airlock (which allows access to the EF), the two windows located above the airlock, the berthing mechanism for the EF (EFBM), an Active Common Berthing Mechanism (ACBM) on the zenith side for berthing the ELM-PS, and a Passive Common Berthing Mechanism (PCBM) used to connect with the port side ACBM of the Harmony module.
 |
| Credits: NASDA |
The EF is a box-shaped structure, which is 5.0 m wide, has a length of 5.2 m, and a height of 3.8 m. The EF has 12 payload attachment locations. Each payload location can accommodate a science experiment that must be conducted in the exposed environment.
Kibo’s robotic arm (JEMRMS) is used for attaching and removing the payloads.
The ELM-PS is a cylindrical structure 4.4 m in diameter and 4.2 m in length. The ELM-PS contains a total of eight rack locations. ELM-PS can be used as storage space for experiments, samples, and spare items.
The ELM-ES provides storage space for up to three payloads. ELM-ES will be attached to the end of the EF. Besides the function of in-orbit exposed storage facility, the ELM-ES can also be used to return scientific payloads to Earth. The ELM-ES is a frame structure 4.9 m wide, with a length of 4.1 m, and a height of 2.2 m.
 |
| Credits: NASDA |
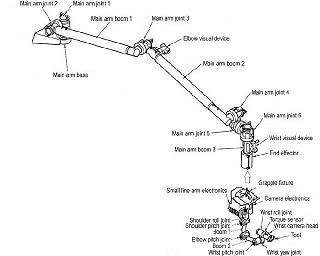
The JEMRMS is a robotic manipulator system. JEMRMS will have two roles: supporting the experiments conducted on Kibo, and assisting with Kibo’s maintenance tasks.
A 10 m long Main Arm (MA), a 2.2 m long Small Fine Arm (SFA), and a robotic control workstation are the components of the robotic manipulator system.
The ICS has two subsystems: a Pressurized Module (ICS-PM) and an Exposed Facility (ICS-EF). The ICS-PM occupies a rack inside the PM, and provides command and data handling functions. The ICS-EF is basically the antenna used for communication.
Kibo is a large structure and more Space Shuttle missions are required to complete the deployment of all the components.
STS-123 Space Shuttle Endeavour delivered the ELM-PS component and ICS-PS to the ISS. JAXA astronaut Takao Doi was part of the STS-123 crew as mission specialist. During the mission, the ELM-PS was berthed to the zenith port of the Node 2 (Harmony) module. The ELM-PS carried the system racks and the experiment racks that are operated in the PM.
 |
| Credits: NASA |
STS-124 Space Shuttle Discovery delivered the PM and the JEMRMS components to the ISS. The JAXA astronaut assigned to STS-124 as mission specialist was Akihiko Hoshide. STS-124 had to perform a number of operations in order to activate and assemble the pressurized components of JEM: installation and activation of PM, rack deployment, installation of JEMRMS, and the relocation of the ELM-PS from the zenith port of Node 2 to the zenith side of the PM.
The EF is the last major component of Kibo that has to be hauled to the ISS. The STS-127 mission will carry the EF, together with the ELM-ES and the ICS-EF components. The completion of Kibo will be done in two steps: the EF will be attached to the PM through the EFBM, and the ELM-ES will be attached to the EF as the last step. JAXA astronaut Koichi Wakata will be on board the ISS to supervise the operation as mission specialist.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency has a web page dedicated to Kibo.















 Subscribe to blog posts using RSS
Subscribe to blog posts using RSS










