NASA dixit:
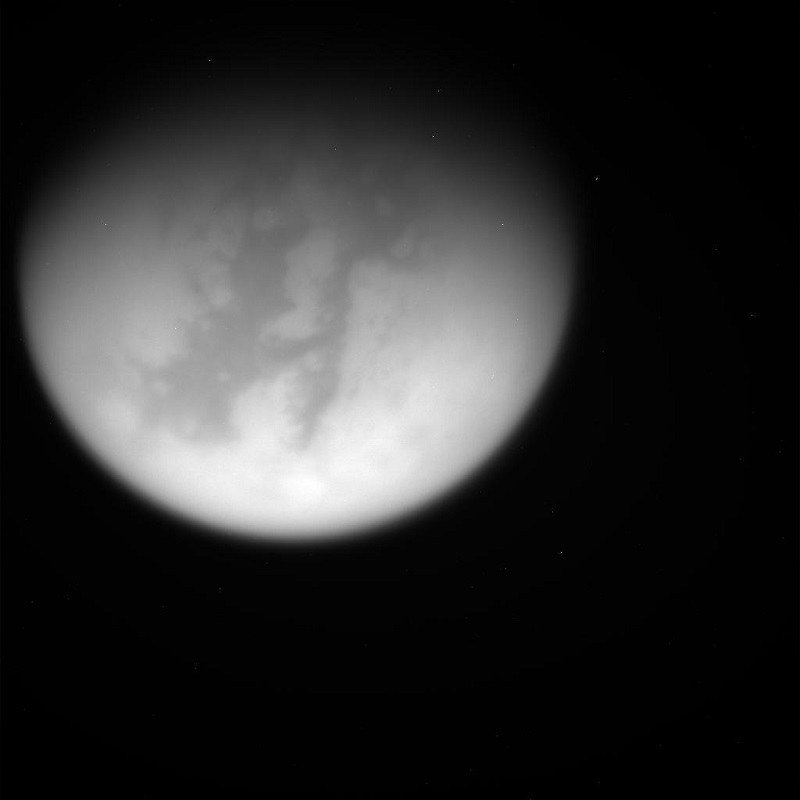
“March 31, 2005. NASA’s Cassini spacecraft successfully flew by Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, at about 2,400 kilometers (1,500 miles) above the surface.”
“After almost 20 years in space, NASA’s Cassini spacecraft begins the final chapter of its remarkable story of exploration: its Grand Finale. Between April and September 2017, Cassini will undertake a daring set of orbits that is, in many ways, like a whole new mission. Following a final close flyby of Saturn’s moon Titan, Cassini will leap over the planet’s icy rings and begin a series of 22 weekly dives between the planet and the rings.
No other mission has ever explored this unique region. What we learn from these final orbits will help to improve our understanding of how giant planets – and planetary systems everywhere – form and evolve.
On the final orbit, Cassini will plunge into Saturn’s atmosphere, sending back new and unique science to the very end. After losing contact with Earth, the spacecraft will burn up like a meteor, becoming part of the planet itself.
Cassini’s Grand Finale is about so much more than the spacecraft’s final dive into Saturn. That dramatic event is the capstone of six months of daring exploration and scientific discovery. And those six months are the thrilling final chapter in a historic 20-year journey.”
Image credit: NASA










 Subscribe to blog posts using RSS
Subscribe to blog posts using RSS










