Asteroid (52246) Donaldjohanson is a small but significant body located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Though it may not have the fame of larger or more compositionally unique asteroids, Donaldjohanson stepped into the scientific spotlight thanks to its pivotal role in NASA’s ambitious Lucy mission — a 12-year journey to explore the Trojan asteroids that share Jupiter’s orbit. Before Lucy reaches its primary Trojan targets, it first encountered Donaldjohanson, making it a key object of study in humanity’s effort to understand the solar system’s early history.
Discovery
Asteroid Donaldjohanson was discovered on March 2, 1981, by astronomer Schelte “Bobby” Bus at the Siding Spring Observatory in Australia. Initially designated 1981 EQ5, the asteroid was later named in honor of Dr. Donald Johanson, the paleoanthropologist best known for co-discovering the fossilized remains of Australopithecus afarensis, famously known as Lucy, in Ethiopia in 1974.
This naming decision was particularly meaningful to NASA, as their Lucy spacecraft, launched in 2021, carries a similar goal: to uncover the fossils of the solar system—namely, the Trojan asteroids, which are thought to be leftover building blocks from planetary formation. Naming the asteroid after Johanson creates a poetic link between the exploration of human origins and the origins of our solar system.
Location and Characteristics
Donaldjohanson resides in the inner region of the main asteroid belt, at a semi-major axis of approximately 2.39 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun. Its orbit is relatively circular and stable, with a low eccentricity and inclination, placing it within the Erigone asteroid family, a large group of stony asteroids in the inner main belt.
Though smaller and less well-studied than some of its larger neighbors, Donaldjohanson’s value lies in its convenience and timing—it is perfectly positioned to serve as a flyby target for the Lucy spacecraft en route to the outer solar system.
The Lucy Mission Flyby
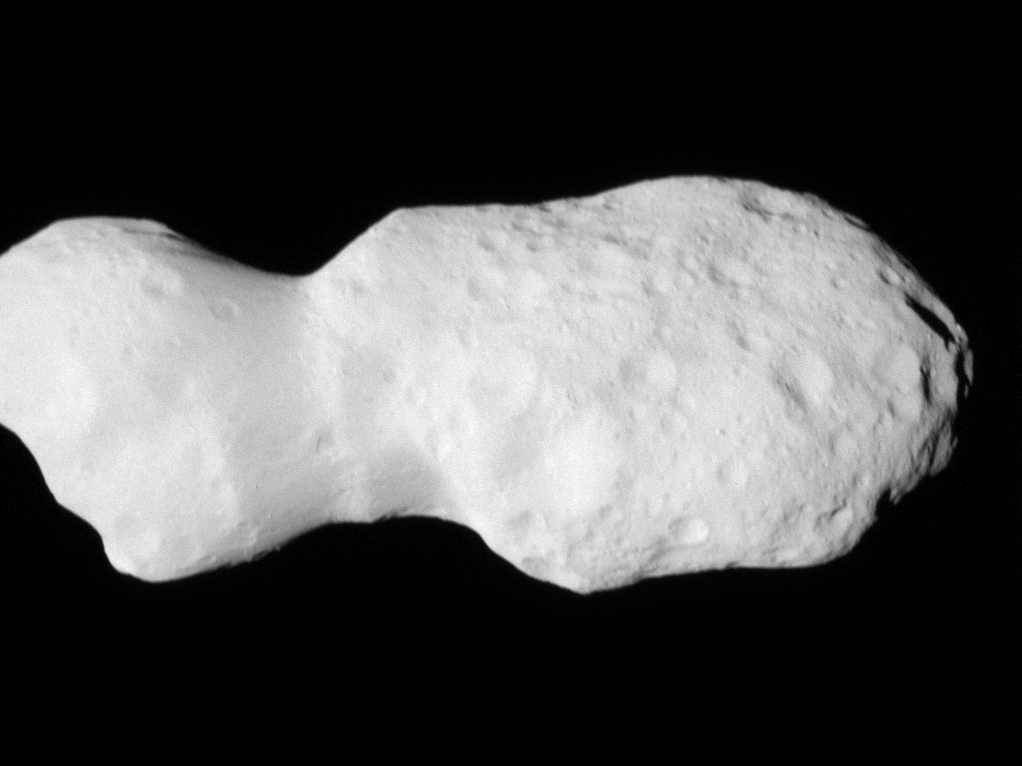
NASA’s Lucy spacecraft has successfully completed a flyby of asteroid Donaldjohanson, providing unprecedented insights into this intriguing celestial body. Lucy performed a close flyby at a distance of approximately 600 miles (960 kilometers), capturing detailed images and data.
The flyby is particularly exciting because very few main belt asteroids have been visited by spacecraft, and each one offers a new data point in understanding the diversity and history of these primitive bodies. By studying Donaldjohanson, Lucy will help bridge the scientific gap between the inner and outer asteroid populations.
During the flyby, Lucy used its three onboard science instruments — L’LORRI (a long-range imager), L’Ralph (a visible and infrared spectrometer), and L’TES (a thermal emission spectrometer) — to examine Donaldjohanson’s surface geology, composition, and thermal properties. In addition to gathering scientific data, the flyby allowed engineers to practice operating the spacecraft’s pointing, tracking, and data-gathering systems ahead of the more complex Trojan encounters.
The flyby revealed that Donaldjohanson is a contact binary asteroid, characterized by two lobes connected by a narrow neck, resembling a peanut or a barbell. This structure suggests a history of two separate bodies gently colliding and merging. The asteroid measures about 8 kilometers in length and 3.5 kilometers at its widest point, larger than previously estimated.
Donaldjohanson’s surface exhibits a complex geology with varying crater densities between its lobes, indicating a diverse collisional history. These observations provide valuable data on the processes that shaped such bodies and, by extension, the early solar system. The successful flyby serves as a critical rehearsal for Lucy’s upcoming encounters with Trojan asteroids near Jupiter, scheduled between 2027 and 2033.
Looking Ahead
While Donaldjohanson is not the primary target of Lucy’s mission, the asteroid plays an essential role in validating the mission’s capabilities and providing early science returns. Its proximity and well-known orbit make it an ideal testbed. Moreover, the data collected during the flyby will contribute to our broader understanding of asteroid families, space weathering, and solar system evolution.
After the 2025 encounter, Lucy will go on to visit eight Trojan asteroids, including Eurybates, Polymele, Leucus, Orus, and the binary pair Patroclus and Menoetius. These objects are expected to reveal new insights into the formation of the gas giants and the migration of planets during the early stages of solar system development.
In this grand journey, asteroid Donaldjohanson acts as the first stepping stone—a humble but crucial waypoint on the path to uncovering our solar system’s ancient past. As such, it not only honors the legacy of scientific discovery associated with its namesake but also propels forward the exploration of space’s most enduring mysteries.









 Subscribe to blog posts using RSS
Subscribe to blog posts using RSS










