NASA dixit:
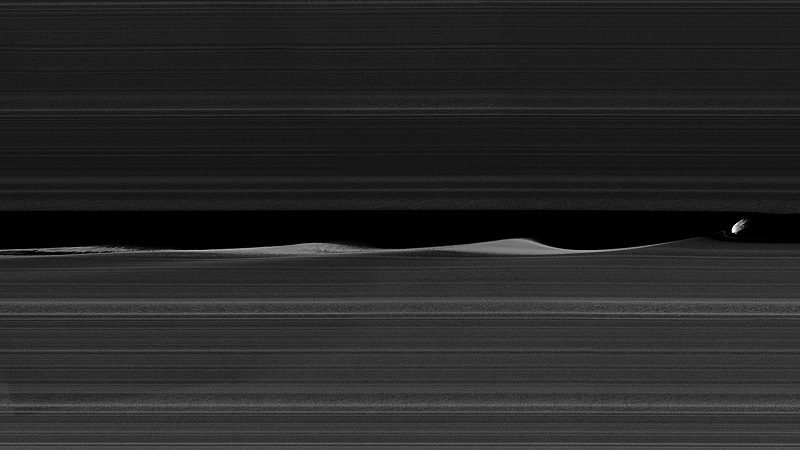
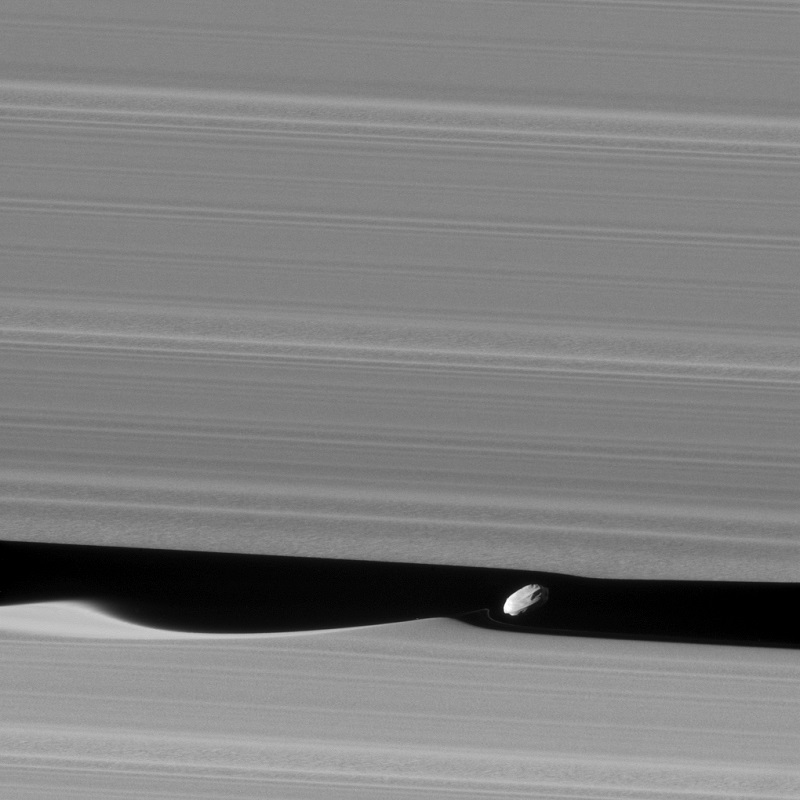
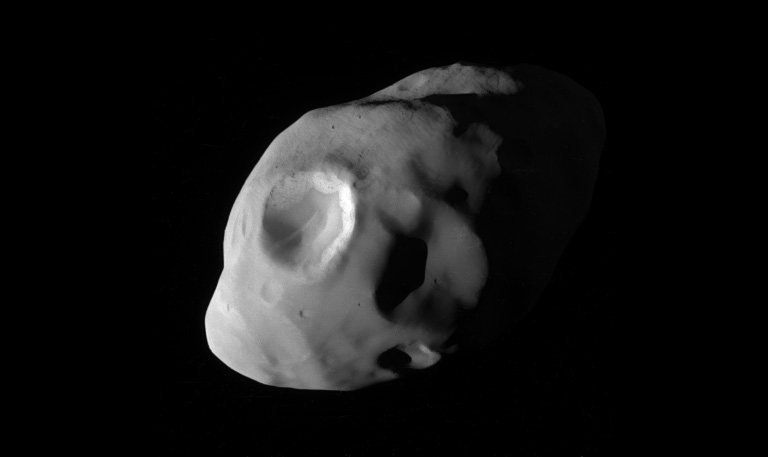
“February 14, 2017. Daphnis, one of Saturn’s ring-embedded moons, is featured in this view, kicking up waves as it orbits within the Keeler gap. The mosaic combines several images to show more waves in the gap edges. Daphnis is a small moon at 5 miles (8 kilometers) across, but its gravity is powerful enough to disrupt the tiny particles of the A ring that form the Keeler gap’s edge. As the moon moves through the Keeler gap, wave-like features are created in both the horizontal and vertical plane.
Images like this provide scientists with a close-up view of the complicated interactions between a moon and the rings, as well as the interactions between the ring particles themselves, in the wake of the moon’s passage. Three wave crests of diminishing sizes trail Daphnis here. In each subsequent crest, the shape of the wave evolves, as the ring particles within the crests collide with one another.
Close examination of Daphnis’ immediate vicinity also reveals a faint, thin strand of ring material that almost appears to have been directly ripped out of the A ring by Daphnis. The images in this mosaic were taken in visible light, using the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera at a distance of approximately 17,000 miles (28,000 kilometers) from Daphnis and at a Sun-Daphnis-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 71 degrees. Image scale is 551 feet (168 meters) per pixel.”
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute













 Subscribe to blog posts using RSS
Subscribe to blog posts using RSS










