NASA dixit:
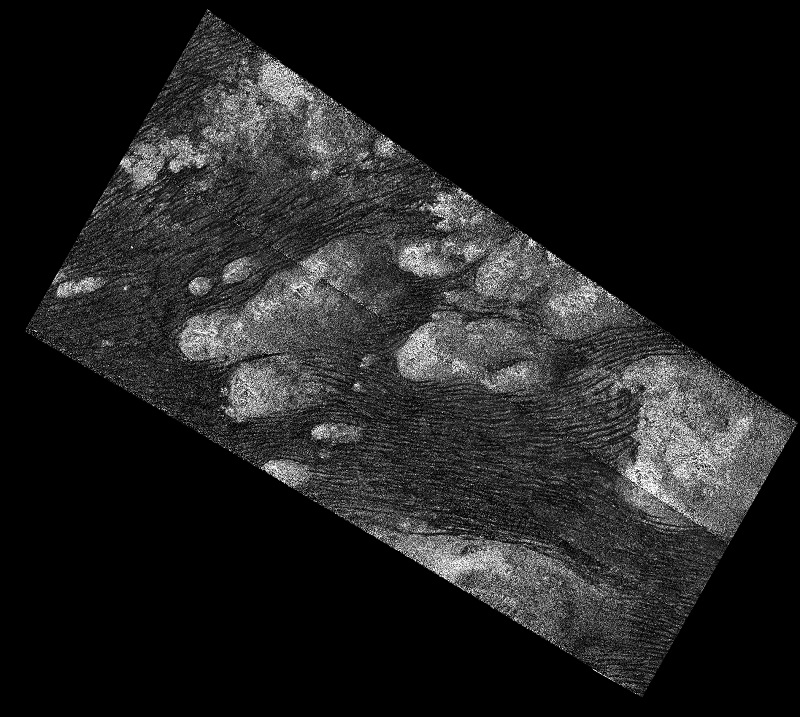
“July 25, 2016. In the Shangri-La Sand Sea on Titan is shown in this image from the Synthetic Aperture radar (SAR) on NASA’s Cassini spacecraft. Hundreds of sand dunes are visible as dark lines snaking across the surface. These dunes display patterns of undulation and divergence around elevated mountains (which appear bright to the radar), thereby showing the direction of wind and sand transport on the surface. Sands being carried from left to right (west to east) cannot surmount the tallest obstacles; instead, they are directed through chutes and canyons between the tall features, evident in thin, blade-like, isolated dunes between bright some features. Once sands have passed around the obstacles, they resume their downwind course, at first collecting into small, patchy dunes and then organizing into larger, more pervasive linear forms, before being halted once again by obstacles.
These patterns reveal the effects not only of wind, perhaps even modern winds if the dunes are actively moving today, but also the effects of underlying bedrock and surrounding topography. Dunes across the solar system aid in our understanding of underlying topography, winds and climate, past and present. Similar patterns can be seen in dunes of the Great Sandy Desert in Australia, where dunes undulate broadly across the uneven terrain and are halted at the margins of sand-trapping lakes. The dune orientations correlate generally with the direction of current trade winds, and reveal that winds must have been similar back when the dunes formed, during the Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods.
North on Titan is up in the image. Radar illuminates the scene from upper right at a 27-degree incidence angle. The image was obtained during the mission’s 122nd targeted Titan encounter.”
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute















 Subscribe to blog posts using RSS
Subscribe to blog posts using RSS










